Martina-DOE Project
Project Description
Optimization of a formulation for the preparation of alginate beads containing Spirulina and magnetic nanoparticles.
Experimental Design (DOE)
To understand how each component influences the final properties of the beads, an Extreme Vertices Mixture Design was employed. This statistical method is highly effective for optimizing formulations where components are subject to specific constraints.
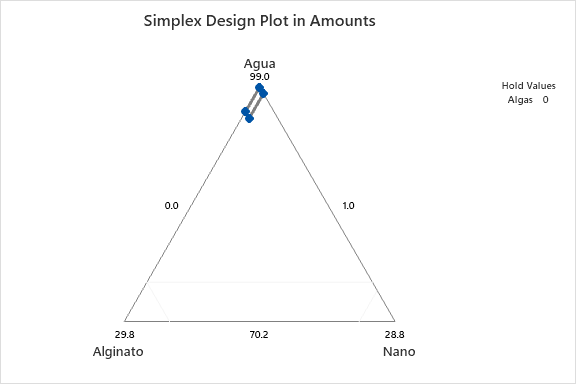
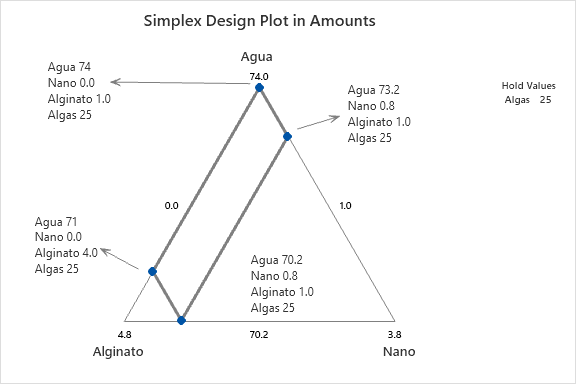
The experiment is based on 4 mixture components and 1 process variable, evaluated over 38 experimental runs to construct a robust predictive model. The components and their respective ranges in the formulation (totaling 100%) are as follows:
- Component A (Water): 70.2% - 99.0%
- Component B (Alginate): 1.0% - 4.0%
- Component C (Nanoparticles): 0.0% - 0.8%
- Component D (Spiruline): 0.0% - 25.0%
The design matrix includes points at the vertices and centroids of the experimental region, with replications at the central point to ensure the accuracy of the quadratic model. Each analysis presented on this page utilizes the data from this DOE to generate contour plots, response surfaces, and statistical models. These results allow for the visualization of how variations in ingredient proportions impact the final properties of the beads, such as swelling capacity or magnetic response.